Overview
The plastic molding process is known to the industry for over a hundred years creating many different types of shapes and designs. Plastic molding also lets companies create mass-market consumer durables at affordable costs reaching billions of people across the world. From basic toothbrushes to large auto and aerospace parts, all made possible through plastic molding. However, to satisfy costs, production & usage needs, the industry has invented different types of plastic molding processes to suit every industrial and consumer requirements. In this article, we are going to discuss various plastic molding processes currently available in the industry.
Types of plastic molding processes
- Compression Molding
- Extrusion blow Molding
- Injection Molding
- Low-Pressure Injection Molding
- Structural foam
- Gas Assisted IM
- Pressure Forming
- Reaction Injection Molding
- Rotational Molding
- Thermoforming
Compression Molding
Compression molding uses matching closed cavity molds under high pressure. The material which is in the form of powder, sheet, semi-liquid etc. is placed into the heated mold. When the mold is closed, the material takes the form of the mold shape under high compression pressure. Once the part is solidified under continued heating, mold is opened to remove the formed part. Fillers and other reinforcing materials are added to the thermosets. The alignment of the fibres and length determines the physical properties of the part.
Materials – EPDM, NBR, PVC nitrile, polypropylene, ABS
Compression molding schematics. Photo credit: Wikipedia
Compression molding
Advantages |
Limitations |
Applications |
|
|
|
Extrusion blow molding
Extrusion blow molding is the process of making hollow parts out of polymer-based raw materials. The essential components of the process are the die head, pressing screw, extruder and mold. The entire set-up is installed on an automatic production system. The heated raw material in viscous form is extruded out into thin flat or circular sheets. Once the sheet is extruded enough to sit inside the mold, then the two halves of the mold are closed, and the air is blown at high pressure into the mold. The heated sheet expands due to the air pressure and takes the shape of the mold.
Materials – HDPE, LDPE, PET
1 Feed from the extruder. 2 Melted plastic. 3 Extruder head. 4 Air tube. 5 Preform (parison) / tubular shape of hot plastic. 6 Mould. 7 Air pressure. 8 (End) product. Source credits: Wikipedia
Extrusion blow molding
Advantages |
Limitations |
Applications |
|
|
|
Injection Molding
Injection molding is the process of manufacturing thermoplastic parts from raw material powder or pellets. The pellets are heated inside the extruder until turned liquid, then forced into the mold cavity thru gates and runners. The mold is cooled by circulating water into in-built cooling channels to accelerate the solidification process. Then mold opens and part is ejected out of the cavity. The parts are designed according to injection molding design methodology for ease of manufacturing.
Materials – ABS, polypropylene, nylon, Acrylic, Polycarbonate, PC-ABS, POM
Injection molding schematics. Photo credit: Wikipedia
Injection molding process
Advantages |
Limitations |
Applications |
|
|
|
Low-Pressure Injection Molding
Structural Foam
The structural foam process is generally used for thermoplastic parts with a cellular core and is made by the injection molding process. A special blowing agent is mixed with the raw material and the rotating screw rotates to move the material forward. Along the path, the mixture is heated, and the chemical agent reacts to form the gas. The entire mixture of gas and bubbles is held in the cylinder under pressure to avoid expanding. Then the mold is then initially filled with the material in smaller quantities to achieve the desired weight needed. Later the pressure is released, and the expanding gas bubbles fill the entire mold completely with the mixture. The mold is cooled down and the part is ejected. The overall injection pressure is much lower than the standard injection molding process.
Material – ABS, PP, PVC, Polyethylene
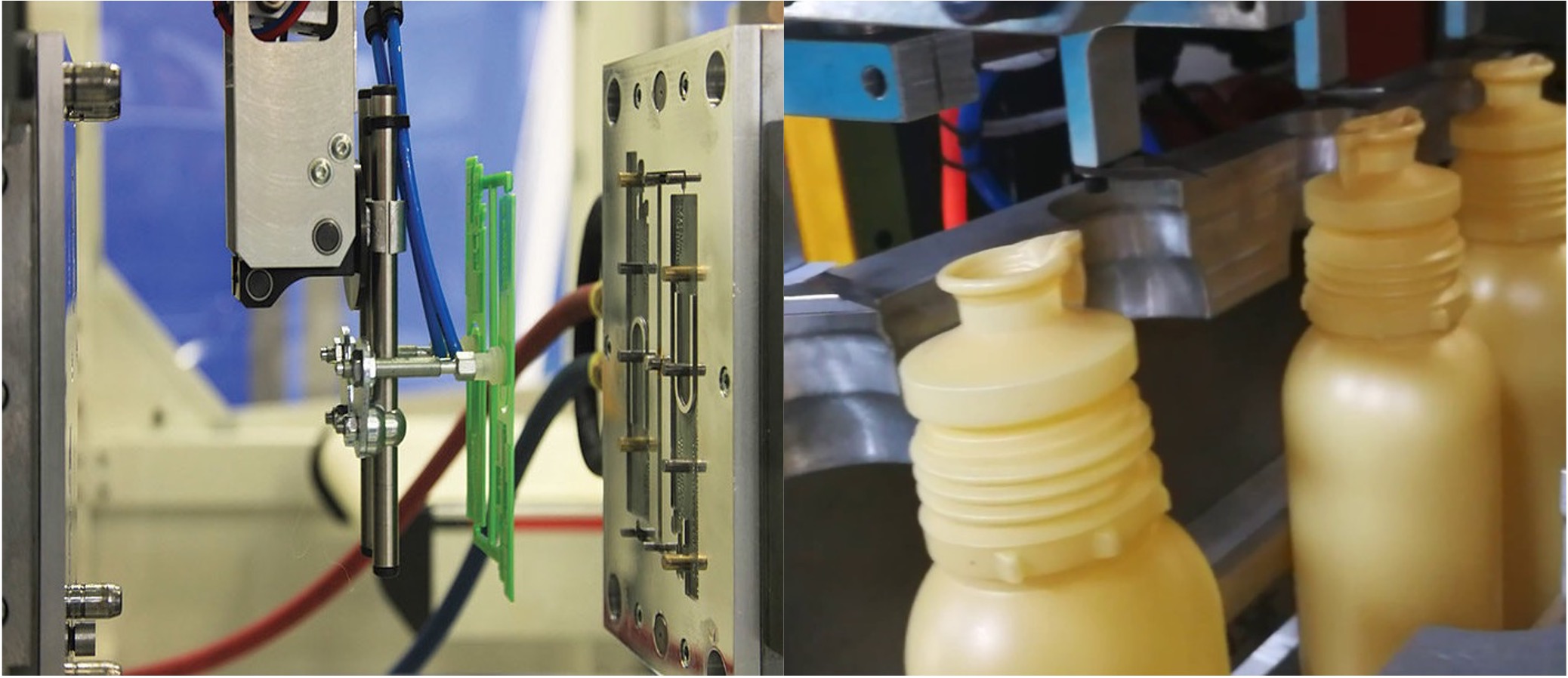
Low-pressure Injection molding schematics. Photo credit: Researchgate
Low-pressure IM Structural foam. Photo credit: LGSovermold
Advantages |
Limitations |
Applications |
|
|
|
Gas-assisted injection molding
Gas-assisted injection molding is to create parts with hollow cavities inside and a low-pressure process than standard injection molding. In this process, a gas injector is fixed on the main nozzle of a standard injection molding machine. The liquid plastic enters the mold partially filling the cavity under normal plunger pressure. Then the gas pressure is applied which enters the cavity centre containing liquid plastic to the outer periphery having softer plastic, thus creating the hollow voids inside the formed part. The created parts are lighter in weight, with lower shrinkages, stress and warpage.
Material – ABS, PP, PC, HIPS, HDPE
Gas-assisted injection molding. Photo credits: PSImoldedplastics
Gas-assisted injection molding
Gas-assisted IM parts. Photo credits: PSImoldedplastics
Advantages |
Limitations |
Applications |
|
|
|
Pressure Forming
Thermoplastic pressure forming is similar to vacuum forming where air or liquid pressure is applied on one side plastic sheet along with vacuum pulling on the other side. The main advantage is that part easily captures tiny features and surface textures at much lower costs than the standard injection molding process. Blowing the plastic sheet prior to forming lets material flow into deeper cavities enabling the formation of large thermoplastic components. Pressure forming is also highly cost-effective for larger parts than those produced by similar manufacturing processes.
Pressure forming process. Photo credits: Productive Plastics
Pressure-formed parts. Photo credits: USKbalaji
Advantages |
Limitations |
Applications |
|
|
|
Reaction Injection Molding
It is a type of injection molding process in which reacting raw material streams are mixed at a controlled temperature. The entire mixture is forced into the mold by the plunger where the polymer is formed inside the mold as a result of the chemical mixture. Commonly used in the automotive industry for plastic parts, however, other sectors are also seeing its increased usage for various consumer and industrial products. Polyurethanes are the market leader in terms of usage, and other materials are also being developed for applications.
Reaction injection molding process. Photo credits: Zeter Mold
Reaction injection molding part. Photo credits: Krauss Maffei
Advantages |
Limitations |
Applications |
|
|
|
Rotational Molding
Rotational molding is low pressure and low initial investment process, especially for larger parts. The entire thermoplastics range and few thermosets are eligible for rotational molding. The raw material in the form of liquid or powder is placed inside the mold. After closing the mold, it is heated and continuously rotated about the vertical and horizontal axis to ensure uniform distribution of raw material over the inner surface of the mold. The mold is then cooled down inside the cooling chamber which solidifies the material. Later, the mold is opened, and part is extracted.
Rotational molding schematics. Photo credits: Wikipedia
Rotational molding process
Rotational molding products. Photo credits: Roto Dynamics
Advantages |
Limitations |
Applications |
|
|
|
Thermoforming
Thermoforming or vacuum forming is the process where the heated polymer sheet is turned into a shape. Two methods are commonly used wrap-around or drape forming and cavity forming. The sheet is first heated and lowered into the mold which takes take the shape of the mold. Vacuum pull is ensuring the sheet perfectly takes the shape of the mold/cavity capturing the features. Part cooling is done by direct contact or water-based cooling. For wrap-around type forming, the part sticks to the surface due to stresses induced by shrinkage. Hence, the designer needs to incorporate draft angles and shrinkage factors into the design for ease of manufacturing.
Thermoforming process schemtics. Photo credits: The Open University
Thermoforming process
Thermoforming products. Photo credits: vacuumformedplastics
Advantages |
Limitations |
Applications |
|
|
|
Created by - 3D SculpLab Team
 3D SculpLab
3D SculpLab