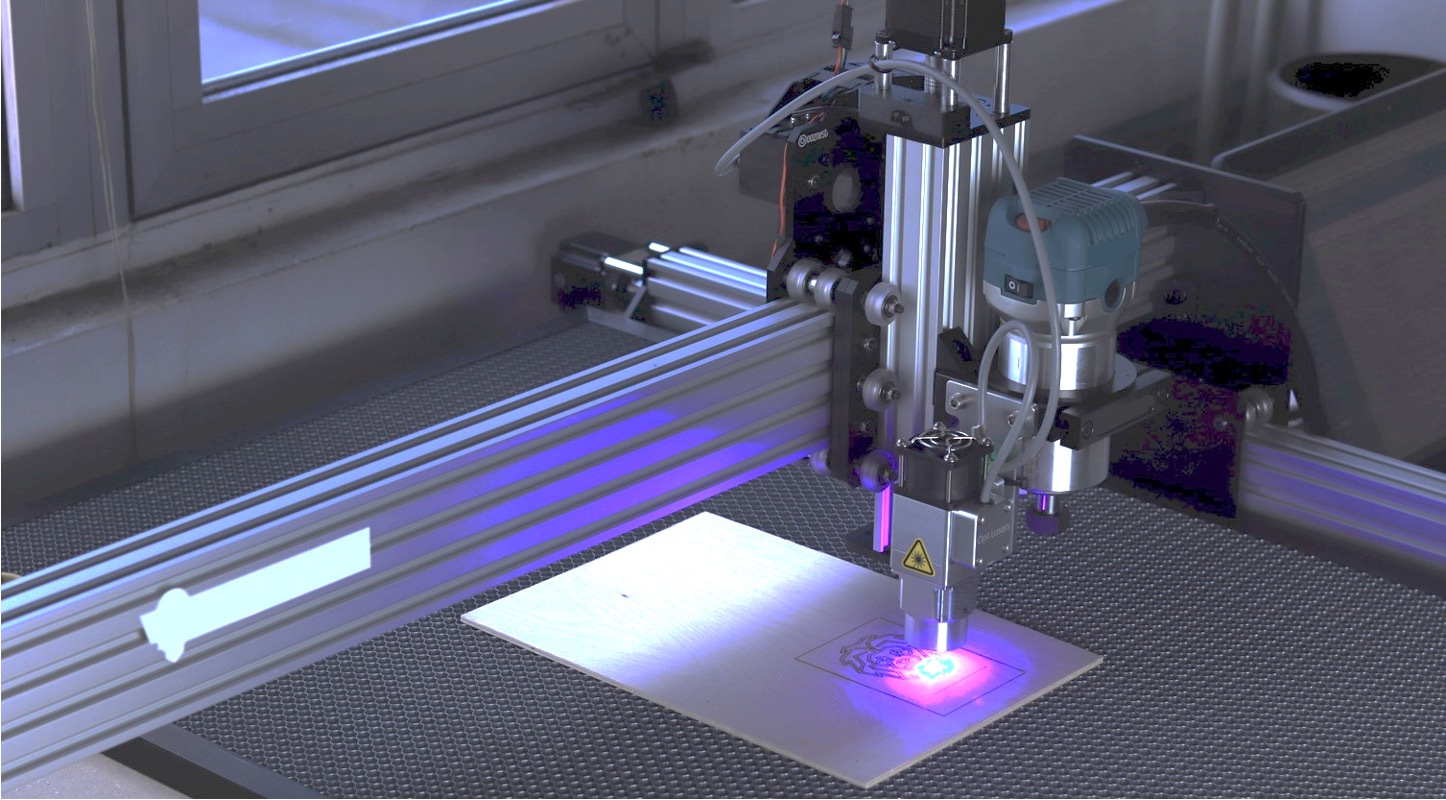
What is laser cutting?
Laser cutting works by way of melting the substance by the application of a high-intensity laser beam into precise shapes letting manufacturers create custom designs. Its versatile technology was developed half a century ago and is useful in many industrial applications due to its capability of producing parts with a high degree of reliability for present-day machine components. Like any other technology, laser cutting also underwent several iterations of improvement over the [period of time enhancing its performance and still continuing to improve. However, there are certain limits to its performance like can cut steel up to certain thinness, beyond that other cutting methods are required such as saw cutting etc.
Lasers can cut a wide array of metals right from various sheets of steel (mild steel, carbon steel, stainless steel) to aluminum and other steel-based alloys. Lasers can also cut non-metal parts such as wool, plastics, ceramics etc. Apart from cutting, lasers are also used for markings, and surface texturing applications.
How does laser cutting work?
A typical laser cutting system projects a beam of high-intensity laser of power between 1 to 3kw and a diameter of around 0.1 to 0.3mm. Output power can be varied depending on the material type and its thickness. Certain materials with high reflection index and high thermal conductivity such as copper alloys and aluminum are not suitable for laser cutting. Also, they need a high power of around 6kw or more to perform the cutting operation.
Laser cutting schematics. Photo credits: Purdue Univ.
Major components of laser cutting machine
- The laser generator – It consists of a vacuum glass tube with two mirrors opposite each other and filled with CO2 and other gasses such as helium, nitrogen and hydrogen. This gas mixture is excited by the electrical discharge that releases energy in the formation of high-intensity light.
- The cutter head – Once the light reaches the cutter head from the laser generator, it gets magnified and focused at a point after passing thru a curved lens. The focus point of the beam should be the surface of the metal for an effective cut in the desired shape. Compresses gas such as nitrogen or oxygen passes thru the outer periphery of the nozzle at high pressure to blow away the melted material. The cutter head is mounted on a cartesian-type gantry which points the cutter head precisely at any location on the surface of the material to ensure a perfect cut.
Types of laser cutting
- Reactive cutting – In this type of cutting high pressure oxygen is blown over the heated surface which initiates oxidation and metal begin to burn. Thus, helping the cutting process by ejecting more energy. Also, the high-pressure oxygen blows away the metal to create a fine cut.
- Fusion cutting process – Ins this process, an inert gas is blown over the molten surface at high pressure to create a cut.
- Direct cutting – In this process, thin sheets of metal are cut by the direct application of very high-intensity laser beam evaporating the material surface, hence generating a cut.
Key applications
- Metal cutting – One of the major applications of laser cutting. The laser can cut a wide range of metals for almost every industrial application. For example, sheet metal blanks are cut precisely by a laser cutting machine. In the shipbuilding industry, section panels are largely cut by lasers.
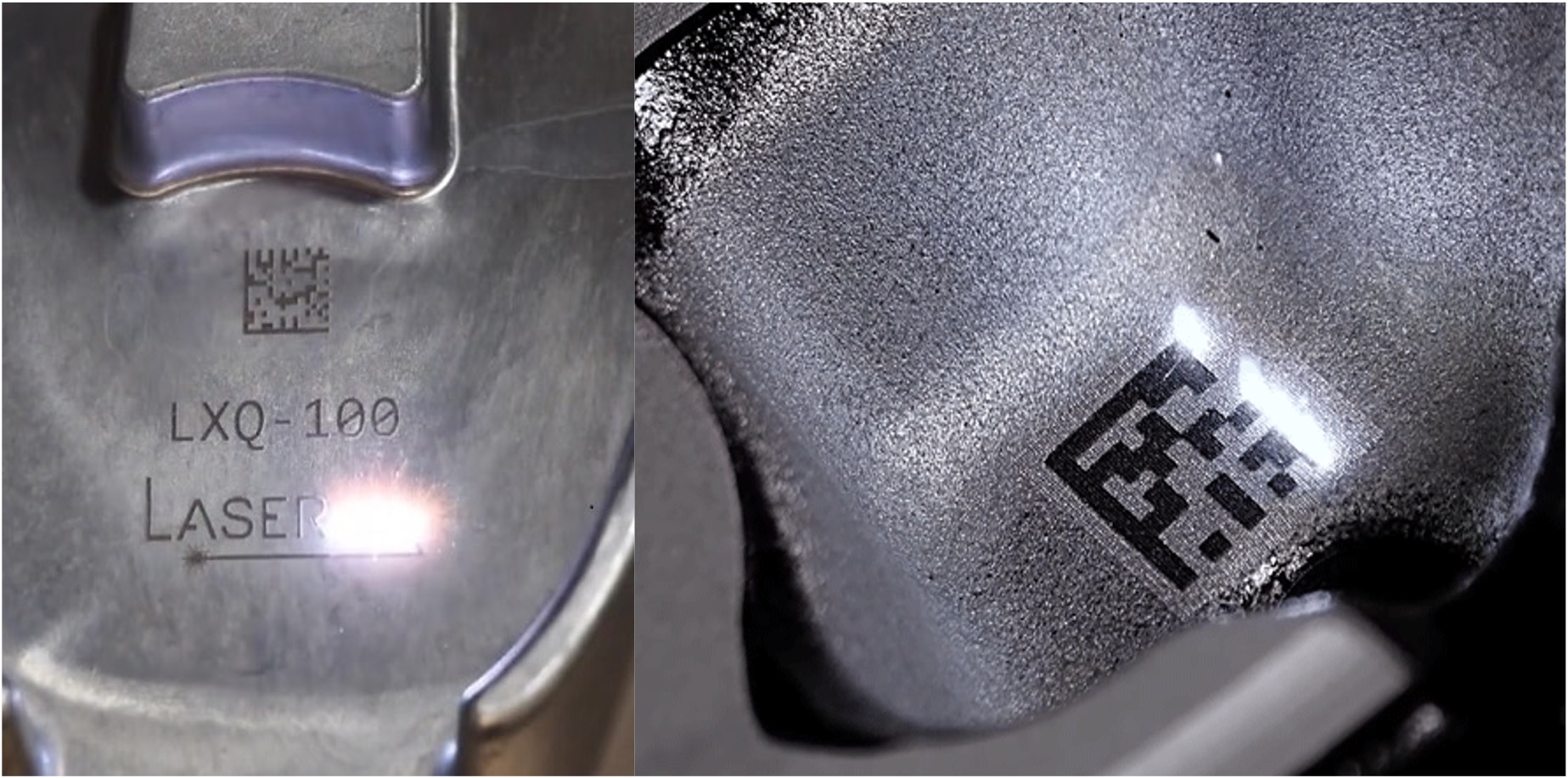
- Laser engraving – In laser engraving, a high-intensity laser evaporates and removes the material from the surface creating a cavity as per the design intent.
- Laser markings – Certain graphics, texts & special symbols can be easily created by lasers on almost all surfaces. The laser does not ablate or created a cavity but alters the properties of the material revealing the markings.
- Prototype development – designers can quickly receive parts by cutting metal or plastic sheets. Later those parts could be welded/assembled together as desired physical evaluation.
- Maintenance and repair – certain parts or machine components which are out of production could be repaired or created cost effectively than other manufacturing processes like CNC, and metal casting.
- Architecture – Large components of public architecture designs can be created.
Typical laser cutting machine
What type of metals laser can cut?
- Steels – Lasers can cut mild steel, carbon steel, stainless steel and some other steel alloys
- Aluminum – Aluminum-based materials are easier to cut than steel because they are less dense, hence, lighter in weight.
- Other materials – Apart from metals, lasers are used to plastics, ceramics, wood etc.
Maximum material thickness
Like any other process, laser cutting has its own limitations. Depth of cut depends upon multiple variables like type of steel, laser power and other things. For example, a 6kw laser can cut stainless steel up to 40mm and high carbon steel up to 25~30mm. Laser with a reduced power output of 4kw can penetrate up to 25mm of stainless steel. Max cutting depth is much more for plastics, and wood since they are less dense and lighter in weight.
Laser power & cutting speed
Laser-cutting machines are commonly available in the range of 3.5kw to 6kw. The maximum cutting depth of a laser cutting system is driven by the material to be cut and laser power. Power less than or equal to 1kw is suitable for light-cutting operations like plastics, wood etc. Not suitable for metal cutting. A 6kw system is most suitable for metal cutting from various sheets of steel to aluminum-based material.
Just like cutting power and the maximum depth of cut, cutting speed is equally important for the entire process. A system which takes less time to finish the operation is always desirable. However, you just cannot cut the material at any speed will lead to poorly finished edges and quality issues later in the cut part. For metals, a high-pressure inert gas is applied to remove the molten material to create the cut.
Laser cutting process. Photo credits: Wattsan
Key advantages
- Fast production speed than the conventional cutting process
- Simplified pre-production process
- High process accuracy and precision
- Contactless process
- Cost-effective than other cutting processes like CNC etc.
- A wide range of materials can be cut
- Fine cutting edges
- Small cutting width
Drawbacks
- Protection is required against toxic fumes and scattered light
- Consumes more energy
- Limited cutting depth across materials
- Can cause burnt edges
Laser cut part. Photo credits: Machinemfg
Conclusion
Laser cutting is versatile technology which can quickly cut various materials in any shape on a linear axis. Metals, plastics, and wood can be cut, engraved or laser marked without much preparation. Cut parts could be directly used for next-level operations. Another benefit is that it is a non-contact thermal manufacturing process that can fabricate complicated designs without the need for special manufacturing tools. In today’s time, lasers have found applications across a variety of industries such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, manufacturing, medical etc. With the advancement in technology, certain challenges could be overcome in future with better machines and improved overall processes. In future, we could also see laser cutting systems being carried by astronauts could be used to cut parts and fabricate structures in space.
Blog created by - 3D SculpLab Team


 3D SculpLab
3D SculpLab