
3D printed parts are indeed quite strong and can be relied upon. There are various ways to optimize the strength of 3D printed according to the application. Earlier 3D printing was only limited to prototype making to check fit and appearance but in the last couple of years, 3D printing is more evolved into making low volume production if not outright large-scale mass production. One question will come to mind if 3D printing could replace other manufacturing technologies (CNC, injection molding etc.)? if 3D printed parts strong and durable than parts made from conventional manufacturing? the answer is no. In this blog, we’re going to talk about more of this.
3D printed parts are more useful during concept/idea validation, market research and custom parts creation. Material type, infill(material fill density), wall thickness are a few of the key factors that decide the strength of 3D printed parts.
Material selection obviously is one of the important factors related to the strength of the printed part. PLA, ABS, polycarbonate, nylon, polypropylene, TPU, PETG are a few of the plastic 3D printing materials.
PLA(Polylactic Acid)
PLA is the most common type of plastic 3D printing material with good tensile strength but brittle in nature. PLA is generally used for basic prototyping, concept validation and limited functional use. PLA durability and strength weaken significantly due to relatively low melting. PLA is made from cellulose hence biodegradable.
ABS(Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is used where resistance to impact force is the key. ABS also offers slight flexibility and bending rather than shattering completely. A high melting point makes ABS stands out to withstand higher operational temperatures.
Polycarbonate
PC is one of the strongest 3D printing materials with very high durability. It has very high impact and heat resistance characteristics.
Nylon
Nylon has high resistance to abrasion, high hardness, excellent toughness and very high tensile strength. Creates rugged parts less prone to wear and tear.
Polypropylene
PP has high toughness and good fatigue resistance. It retains its share after bending & flexing.
TPU(Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
TPU is also referred to as in between rubber and plastic. It is flexible in nature and highly durable.
PETG(Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
PETG when it comes to 3D printing, PETG is usually used for parts with complex geometry and designs. PETG is more durable, high density and more rigid than other 3D printing materials.
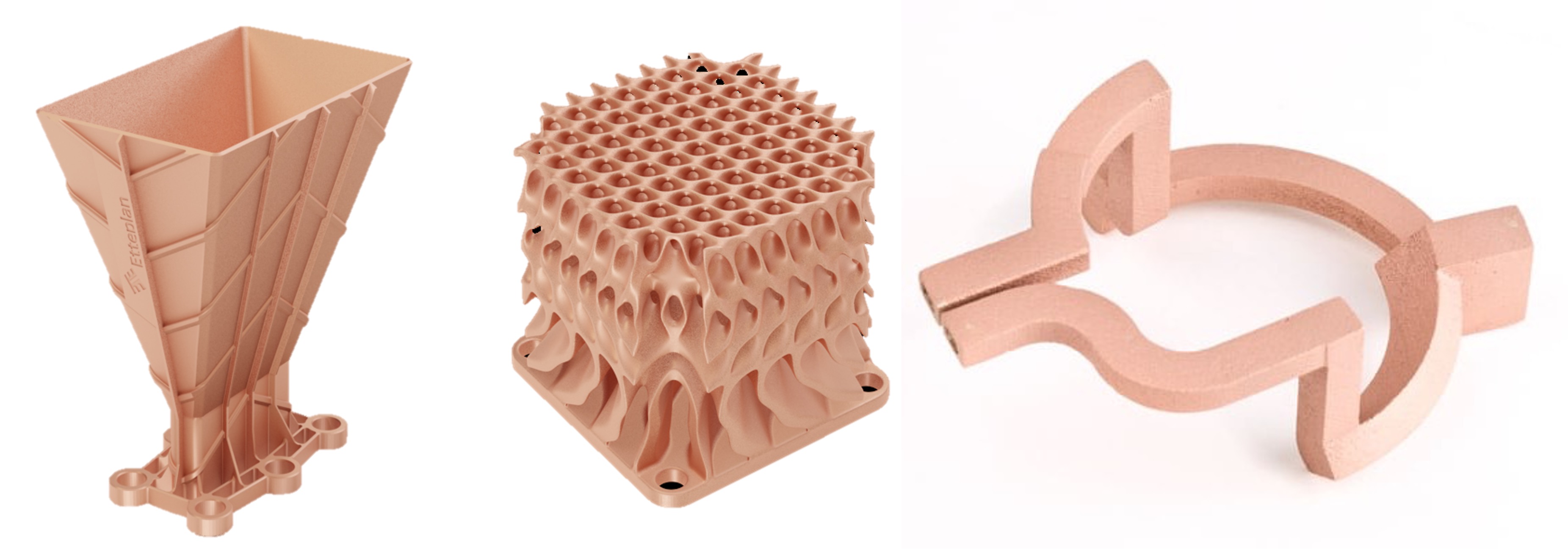
How to make 3D printing parts stronger?
Infill
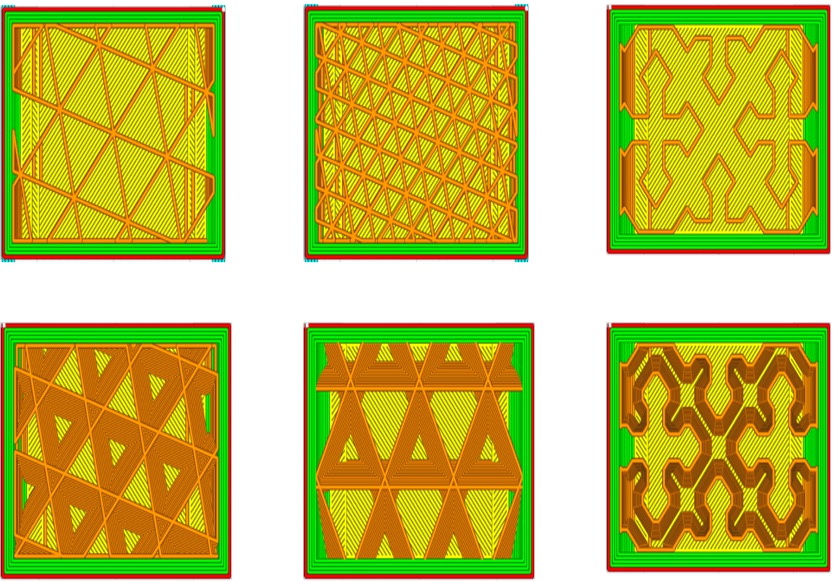
Infill is the material filled inside the 3Dprinted part or how much material is filled inside the shell. The percentage of infill can be controlled thru the software according to the application requirement. 100% infill creates a solid part with a relatively high degree of strength but also costs more. Applications which doesn’t demand that much strength are set with lower infill starting from 25% up to 100%. Plenty of infill patterns are available that could be applied according to the requirements like grid pattern, honeycomb, concentric, zig-zag etc.
Wall thickness
Wall thickness of a 3D printed part is directly proportional to the strength, durability and weight-bearing capacity. A thicker wall means a strong and rigid part, but wall thickness cannot go beyond a certain point. Extra thickness may create internal stresses inside the part that could result in warping and print failure.
Layer direction
Layer direction is one of the most important factors determining the strength of the part. Part can sustain greater forces along the lines of layers than normal to the direction of the layers or print direction. The reason is, the layers are squeezed one above another step by step and the bonding strength between the layers is a weak point. Too many forces acting normal to the layer direction may rip the part apart. This is a unique tendency of any 3D printed part and is also known as anisotropic behaviour.
Conclusion
Smart design incorporating DfAM and the right selection material could create stronger parts. Also, the right build strategy will ensure adequate strength in the force applied directions. Hence, the time has come for every designer to take AM and its various design aspects seriously and leverage the design freedom offered by AM to make better products.
Blog created by - 3D SculpLab Team


 3D SculpLab
3D SculpLab