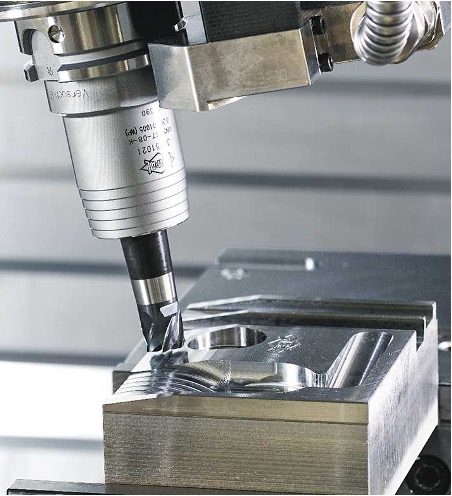

CNC machining is the most popular manufacturing technology for making high precision parts for functional analysis, prototyping, and regular production, especially for metal parts. While designing the parts for CNC machining, a designer needs to remember few important tips to generate a successful design from the manufacturing point of view. Poorly designed parts may lead to cost overruns, longer lead time, design rectifications or simply cannot be machined.
Here are a few important design rules to which can improve the CAD part for CNC machining.
Avoid too small features
Features smaller than 2.5mm cannot be machined since most CNC machines tools can be machined up to 2.5mm. Features below 2.5mm need special tools and processes which will lead to additional cost impact.
Use standard hole size
Nonstandard hole sizes are sometimes difficult to machine and may need special tools to create them with an extra cost overrun and time. Holes matching with the drill bit size are easily drilled and save machine time. if a certain hole size is close to some drill bit size, then it is recommended to match the hole with the size of the bit. For multiple holes try to keep the same hole sizes to avoid multiple tool changes.
Limit thread length
It is recommended to keep thread length up to 2.5 to 3 times of the thread diameter while designing the tapped hole. Thread length beyond three times the diameter is sometimes not needed and just unnecessary. As designer should avoid deep taps because of chances of vibration and tool deviation which results in the defective tap. For blind holes, it is recommended to add extra unthreaded length towards the hole bottom to let the tapping tool fully create the required thread length.
Avoid too thin walls
Extremely thin walls should be avoided while designing parts for CNC machining. Lowering the wall thickness disproportionately affects the stiffness negatively. According to studies, stiffness is directly proportional to the thickness of the material. Lower thickness may compromise the part accuracy due to unavoidable vibrations during the machining process. Recommended minimum wall thickness for metals is 0.8mm and for plastics 1.5mm. If the thin wall design is a necessity, then the designer should opt for other manufacturing processes like sheet metal fabrication.
Avoid partial holes
Partial holes are those where the hole axis is outside the periphery. These types of holes should be avoided by the designer because this may make the tooltip deviate from its axis. If the partial hole is a must, then it is advised to keep the tool axis within the part periphery so that the max hole lies on the part.
Avoid too deep cavities
Deep cavities are those which are more than five to six times deep of the tool diameter. It is advisable to keep the width to depth ratio of any cavity, maximum depth should be up to four times the cavity width. Too deep cavities result in chip accumulation, chances of tool deviation, and tool damage.
Avoid too much focus on aesthetics
A designer should consider how much material will be removed and which process would be applied (3 axes or 5 axes CNC) before creating the part or part feature. Designers should focus on the accuracy of the part than aesthetics value. Aesthetics could be enhanced later during post-processing such as electroplating, polishing etc.
Text design
When adding text is necessary, the designer should go for engraved text than embossing to save on time and money as less material is wasted for the engraved process.
Another option for adding texts, texts can be painted on the surface of the machined part during post-processing. This can save machining time and cost.
Avoid sharp internal edges
Sharp internal corners are unachievable because milling is done with round tools. It is recommended to apply the largest possible radius for ease of manufacturing. Thumb rule, the corner radius should be equal to or more than the tool radius. Drill a hole along the corner if another part with a sharp corner needs to fit inside the cavity.
Apply tolerance wherever required
While designing any part for CNC, designers add tolerance for certain dimensions which are critical to the application or assembly. Applying tolerances everywhere will add up to the final cost of machining, hence it is advised to add tolerance wherever needed.
Avoid features that cannot be machined
A designer should always keep in mind that the part or feature he is creating should be machinable. Avoid creating impossible to machine features. if such features are a necessity, then go for other processes like electrode discharge machine (EDM).
CNC Turning
Avoid too long and thin part
The too long and thin parts will cause vibration and unstable spinning. The thumb rule is to keep the length to diameter ratio at 8:1 or less.
Avoid thin walls
Just like CNC milling, avoid thin walls.
Additional Tips
Easy machine set-up
While designing the part, a designer should also think about how the part would be held on the machine bed/chuck. One of the easiest ways to held part is thru vice if there are a planner and parallel side surfaces. Non-planer surfaces/edges require a special set arrangement which adds to the overall cost. Make sure all the features could be machined easily and within the reach of the tool in one direction. Too thin parts are difficult to hold and are susceptible to warping/bending.
Material selection
Select the material which matches the requirement. Harder material rapidly increases the machining time due to slower process and increases the cost. Also, nonstandard material increases the cost and time since they are harder to procure and needs special machining preparations. Hence, designers should select wisely select the material according to the actual requirement. For example, selecting softer but hard material like aluminum 6061 significantly reduces the machining time and cost.
Tool changes
Tool changes are required to initiate a new operation. Too many tool changes increase the cost and time of the part. A designer should create a part keeping the number of tool changes to a minimum. For example, the same hole or tap size will need only one drill tool and one tap tool only.
Add fillet in internal cavities
Internal fillets are easier to carve than chamfer because round tip tools can be used.
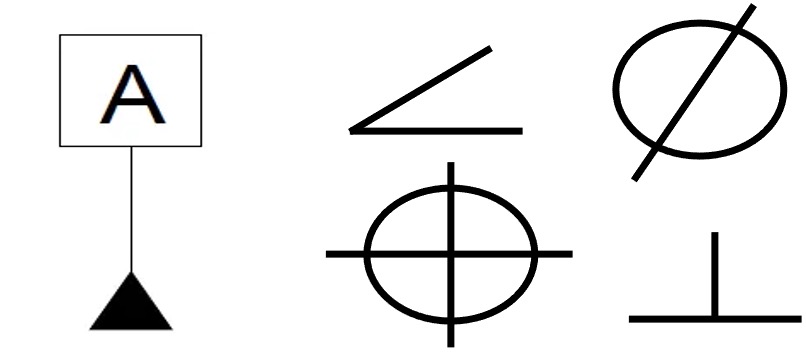
 3D SculpLab
3D SculpLab